This article details the extensive adverse effects of alcohol on various bodily systems, including the brain, liver, heart, digestive system, and immune system, while also increasing cancer risk and impacting skin and hair. It highlights both short-term and long-term consequences such as cognitive decline, mental health issues, liver damage, and metabolic problems. Ultimately, the article emphasizes the importance of understanding these risks and offers pathways to recovery and support for those looking to address their alcohol consumption.
Are you questioning your relationship with alcohol and your health? Whether you’re in recovery, part of Alcoholics Anonymous, sober curious, or concerned about your drinking habits, understanding the effects of alcohol on the body is the first step toward making informed decisions about your health. Below, learn more about the often-overlooked realities of alcohol consumption, offering insights and support for those seeking a healthier path.
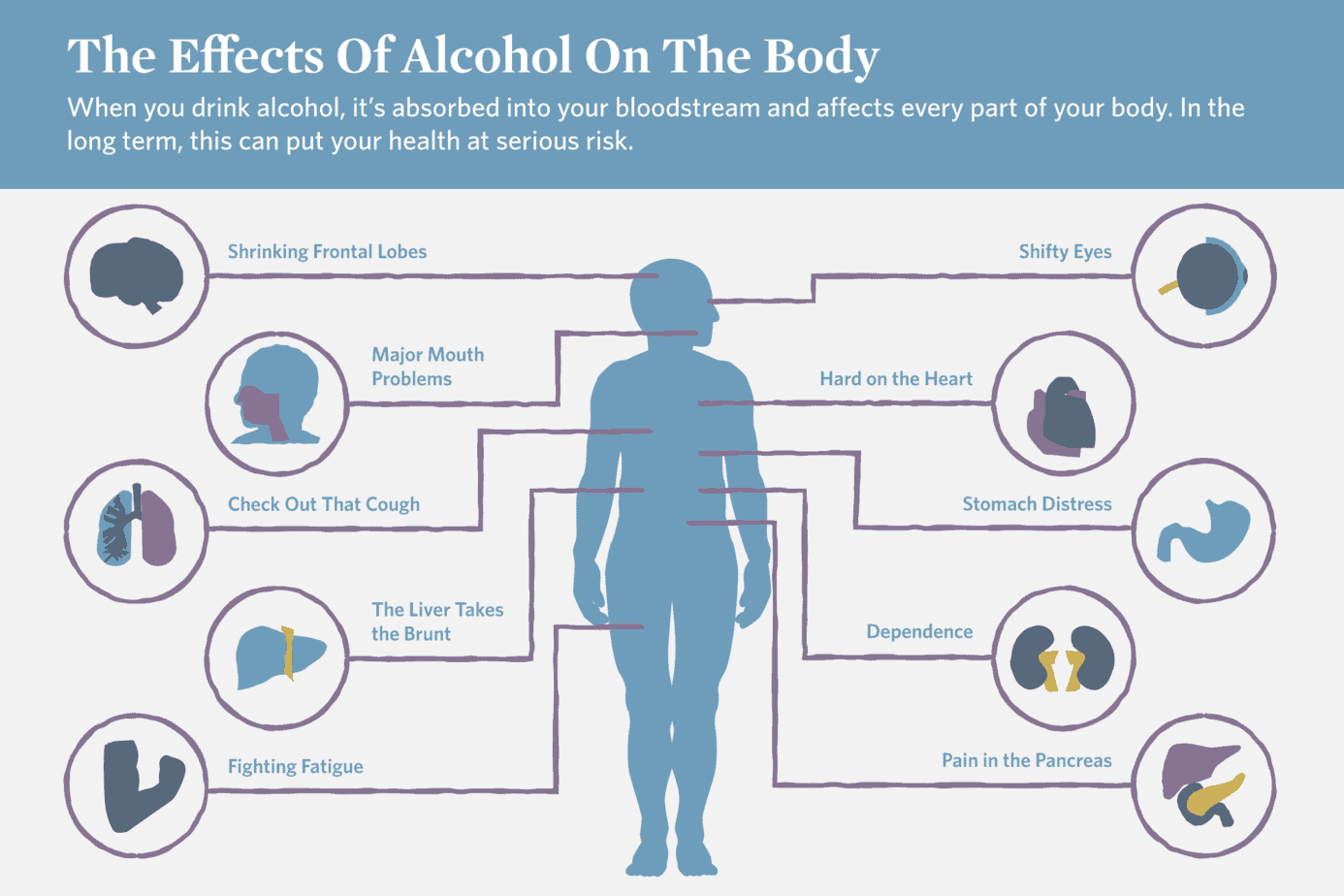
1. Brain Damage and Cognitive Decline
One of the most alarming long-term effects of alcohol consumption on organs is its impact on the brain. Alcohol is a neurotoxin, meaning it can directly damage brain cells. Research shows that chronic alcohol use can lead to cerebral atrophy, which is the shrinking of brain tissue. Studies have found degeneration of neurons in the frontal cortex, similar to what’s seen in Alzheimer’s disease, and damage to the corpus callosum, which connects the brain’s two hemispheres.
- The impact: This damage can manifest as accelerated cognitive decline, affecting memory, learning, and decision-making. Heavy drinkers may experience a 30 percent faster decline in working memory compared to those who abstain.
- Hope for the future: While the damage can be significant, remember that the brain has some capacity to heal, especially with abstinence and proper support.
2. Alcohol’s Impact on Mental Health
Understanding alcohol’s impact on mental health is crucial. While alcohol might initially seem like a stress reliever, it can worsen anxiety and depression over time. Alcohol disrupts the balance of neurotransmitters like GABA and glutamate, leading to a cycle of dependence and worsening mental health symptoms.
- The impact: Alcohol use is linked to increased rates of depression, anxiety, and even suicidal thoughts. It can also interfere with the effectiveness of mental health medications.
- A growing trend: It’s encouraging to see that 36 percent of Gen Z cite mental health as their primary reason for choosing alcohol abstinence, according to recent studies.
3. Alcohol & The Liver
When considering how alcohol impacts the liver and brain, the liver’s plight is particularly dire. Alcohol is a leading cause of cirrhosis worldwide. The liver processes alcohol, and excessive drinking can overwhelm its capacity, leading to inflammation, scarring, and eventually liver failure.
- The impact: Alcohol-associated cirrhosis has a grim prognosis, and many do not survive past the five-year mark without a liver transplant.
- The numbers: Epidemiological models predict a staggering 77 percent increase in the incidence of decompensated cirrhosis by 2040.
4. Heart Health: A Complex Relationship
Alcohol and its effects on the cardiovascular system present a confusing picture. Moderate drinking (1-2 drinks per day) has been linked to a reduced risk of coronary heart disease. However, this benefit disappears with heavier drinking.
- The impact: Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to cardiomyopathy (weakening of the heart muscle), arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats), and high blood pressure.
- A troubling trend: Recent data shows an increase in alcohol-attributable cardiovascular deaths, highlighting the dangers of heavy drinking.
5. Digestive Disruption: From Gastritis to Pancreatitis
The short-term effects of alcohol on the digestive system can be felt almost immediately. Alcohol irritates the lining of the stomach and intestines, leading to inflammation and discomfort.
- The impact: Binge drinking can cause acute erosive gastropathy, resulting in stomach pain and bleeding. Chronic alcohol use can also damage the pancreas, leading to pancreatitis, a painful and potentially life-threatening condition.
- Rising hospitalizations: Hospitalizations for alcohol-attributable pancreatitis have increased significantly, especially among young people.
6. Immune System Suppression: Leaving You Vulnerable
Alcohol’s impact on the immune system is significant. Chronic alcohol consumption weakens the immune system, making you more susceptible to infections.
- The impact: Alcohol impairs the function of immune cells, increasing the risk of bacterial pneumonia, tuberculosis, and viral infections like COVID-19.
- Increased risk: Heavy drinkers are at a much higher risk of developing serious infections.
7. Cancer Risk: A Clear and Present Danger
Alcohol is a known carcinogen, meaning it can cause cancer. The 2025 Surgeon General’s Advisory confirms that alcohol contributes to approximately 100,000 cancer cases annually in the U.S.
- The impact: Alcohol is linked to an increased risk of cancers of the mouth, throat, esophagus, liver, breast, and colon.
- The danger of combining: Combining alcohol with tobacco dramatically increases the risk of certain cancers, such as oropharyngeal cancer.
8. Skin and Hair Problems
The surprising effects of alcohol on skin and hair are often overlooked. Alcohol can cause facial flushing, broken blood vessels, premature aging, and hair loss.
- The impact: Alcohol depletes vital nutrients needed for healthy skin and hair, leading to dryness, wrinkles, and thinning hair.
- Inflammation: Alcohol triggers histamine release, causing skin inflammation and redness.
9. Weight Gain and Diabetes Risk
Physical consequences of chronic alcohol abuse extend to your metabolism. Heavy drinking can lead to weight gain, insulin resistance, and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- The impact: Alcohol disrupts hormone balance and interferes with the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar.
- Hidden calories: Alcoholic beverages are often high in calories, contributing to weight gain and metabolic problems.
10. The Road to Recovery: Finding Support and Hope
Understanding the negative effects of daily alcohol intake on your body is crucial, but it’s equally important to know that recovery is possible.
- The power of support: Both Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) and SMART Recovery groups can help support abstinence and long-term recovery
- Embracing sobriety: The “sober curious” movement is gaining momentum, with many people consciously choosing to reduce or eliminate alcohol from their lives.
What are the top 10 effects of alcohol on the human body? As we’ve explored, alcohol’s effects are far-reaching and can have devastating consequences on your physical and mental health. The drinking effects are not worth the alcohol risks.
Taking Action: Your Path to a Healthier Future
If you’re concerned about your alcohol consumption, remember that you’re not alone. Here are some steps you can take:
- Talk to your doctor: Discuss your drinking habits and any health concerns you may have.
- Seek professional help: Consider therapy or counseling to address underlying issues contributing to alcohol use.
- Join a support group: AA and other support groups provide a safe and supportive environment for sharing experiences and building connections.
- Explore alternative beverages: Experiment with non-alcoholic options and discover new ways to socialize and relax without alcohol.
The effects of alcohol on the body are serious, but with awareness, support, and a commitment to change, you can reclaim your health and wellbeing. If you or someone you know is struggling with alcohol abuse, Mountainside can help. From detox to aftercare, we provide comprehensive and individualized treatment plans for those with substance abuse struggles. Speak with an admissions counselor today!
If you or a loved one is struggling with addiction, Mountainside can help.
Click here or call (888) 833-4676 to speak with one of our addiction treatment experts.

 By
By 




